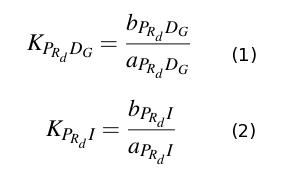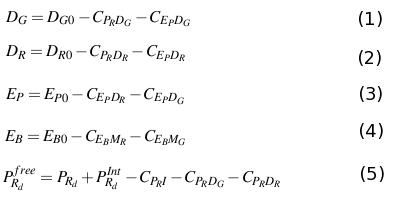Team:Bologna/Modeling
From 2009.igem.org
Marco.cavina (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template:BolognaTemplate}} | {{Template:BolognaTemplate}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
<html><center> | <html><center> | ||
<font face="Dom Casual" font size="3" color="#000000"><i><b>"The theory is when you know everything and nothing works. Practice is when everything works and nobody knows why. We have put together the theory and practice: there is nothing that works ... and nobody knows why."</b> | <font face="Dom Casual" font size="3" color="#000000"><i><b>"The theory is when you know everything and nothing works. Practice is when everything works and nobody knows why. We have put together the theory and practice: there is nothing that works ... and nobody knows why."</b> | ||
| Line 7: | Line 10: | ||
</center></html> | </center></html> | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| - | |||
| - | + | = Introduction = | |
| - | < | + | <font size="4" color="#000000"> |
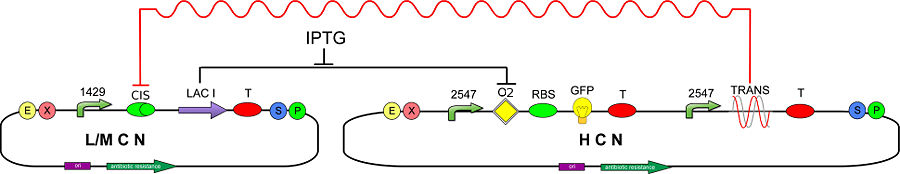
In order to test and characterize our T-REX device, we developed the following genetic circuit (Fig. 1): | In order to test and characterize our T-REX device, we developed the following genetic circuit (Fig. 1): | ||
| - | </font | + | </font> |
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| - | [[Image:circuit2OK.jpg|center|900px|thumb|<center>Figure 1 - Genetic Circuit to test CIS and TRANS' mRNA | + | [[Image:circuit2OK.jpg|center|900px|thumb|<center>Figure 1 - Genetic Circuit to test CIS and TRANS' mRNA functionality</center>]] |
| - | <br> | + | <br><br> |
| + | |||
= Mathematical Model = | = Mathematical Model = | ||
<br><font size="4"> | <br><font size="4"> | ||
| Line 21: | Line 24: | ||
In this context, RNA polymerase and ribosome perform enzymes' role, while gene promoter and RBS sequence act as substrates. | In this context, RNA polymerase and ribosome perform enzymes' role, while gene promoter and RBS sequence act as substrates. | ||
<br> The interaction between enzyme and substrate leads to the formation of a complex, yielding to the final product: mRNA for the RNA polymerase - promoter complex and ribosome - RBS sequence complex. | <br> The interaction between enzyme and substrate leads to the formation of a complex, yielding to the final product: mRNA for the RNA polymerase - promoter complex and ribosome - RBS sequence complex. | ||
| - | |||
</font> | </font> | ||
| - | + | <br><br> | |
| - | + | ||
| + | =Reactions= | ||
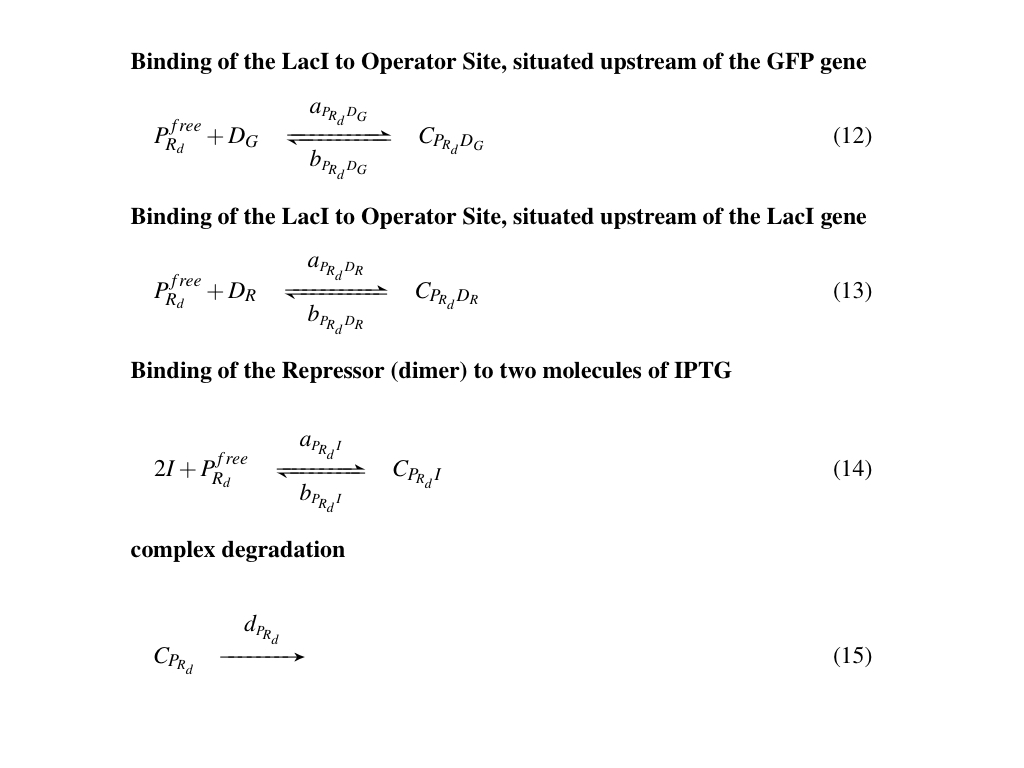
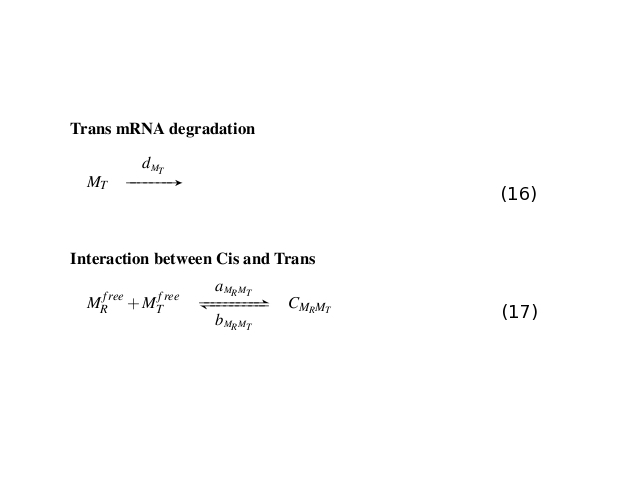
Here below are shown all the reactions occurring the circuit (Fig. 1 and Fig. 2). | Here below are shown all the reactions occurring the circuit (Fig. 1 and Fig. 2). | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | [[Image:Modello1.png|center|940px||thumb|Figure 1: GFP transcription and | + | [[Image:Modello1.png|center|940px||thumb|Figure 1: GFP transcription and translation (left); LacI transcription, translation and dimerization (right) ]]<br> |
{|align="center" | {|align="center" | ||
|[[Image:Pag3.jpg|450px|thumb|Figure 2: Other Chemical Reactions]] | |[[Image:Pag3.jpg|450px|thumb|Figure 2: Other Chemical Reactions]] | ||
| Line 33: | Line 36: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| - | + | =Differential Equations= | |
| - | + | ||
Differential equations, that describes the project, are obtained appling the law of mass action at the reactions above. | Differential equations, that describes the project, are obtained appling the law of mass action at the reactions above. | ||
[[Image:Differentialequations3.jpg|940px||thumb| Figure 4. Differential Equations]] | [[Image:Differentialequations3.jpg|940px||thumb| Figure 4. Differential Equations]] | ||
| Line 40: | Line 42: | ||
[[Image:Constants3.jpg|center|500px||thumb|Figure 6: Equilibrium Constants]] | [[Image:Constants3.jpg|center|500px||thumb|Figure 6: Equilibrium Constants]] | ||
[[Image:Algebricalconstrain2.jpg|center|650px||thumb|Figure 7: Algebraic Constrains]] | [[Image:Algebricalconstrain2.jpg|center|650px||thumb|Figure 7: Algebraic Constrains]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Simulations= | ||
Revision as of 00:25, 22 October 2009
| HOME | TEAM | PROJECT | SOFTWARE | MODELING | WET LAB | PARTS | HUMAN PRACTICE | JUDGING CRITERIA |
|---|
A. Einstein
Contents |
Introduction
In order to test and characterize our T-REX device, we developed the following genetic circuit (Fig. 1):
Mathematical Model
The mathematical model is based on the law of mass action, and the processes involved in gene expression, that is transcription and translation, are considered similar to enzymathic reactions.
In this context, RNA polymerase and ribosome perform enzymes' role, while gene promoter and RBS sequence act as substrates.
The interaction between enzyme and substrate leads to the formation of a complex, yielding to the final product: mRNA for the RNA polymerase - promoter complex and ribosome - RBS sequence complex.
Reactions
Here below are shown all the reactions occurring the circuit (Fig. 1 and Fig. 2).
Differential Equations
Differential equations, that describes the project, are obtained appling the law of mass action at the reactions above.
 "
"